Executive Summary
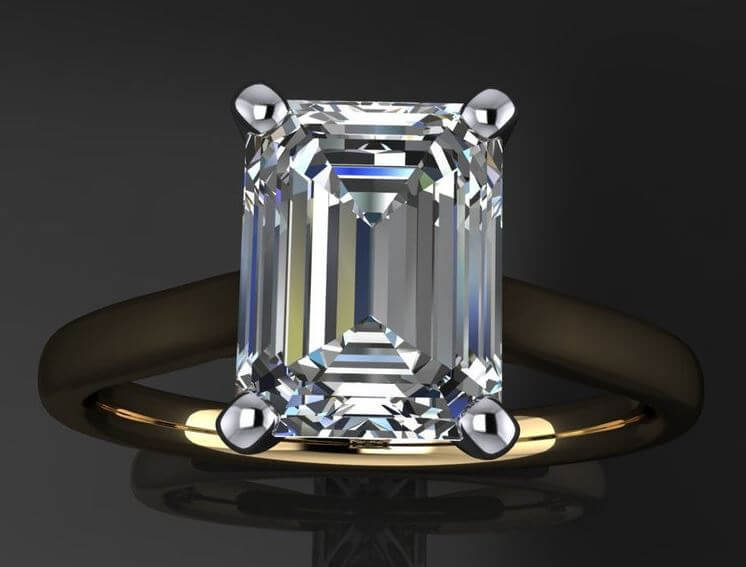
The emerald diamond is a rectangular-shaped diamond with 50 – 58 facets. The number of facets may differ among different emeralds and it basically depends on the pavilion and the number of rows on its crown. The length to width ratio that is appropriate for the emerald cut is 1.5 to 1 or 1.7 to 1. The emerald diamond is a less brilliant diamond than many other diamonds like the round diamond and princess diamond. This is because the diamond wasn’t cut to emphasize brilliance but to emphasize clarity. It, however, has a more subtle sparkle than the other diamonds. The ideal depth of the emerald diamond cut is between 60 to 65% and the table also ranges from 61 percent to 68 percent.
The emerald diamond is a step cut diamond known to produce an effect known as the “hall of mirrors” effect. This effect or illusion creates flashes of white light that are bright when compared to the dark planes that are within the steps of the diamond.
It is an unforgiving cut that requires a high level of perfection. Impurities and inclusions in the diamond are noticed very easily, so it requires a higher clarity and color grade than most other diamonds require. The attractiveness of the cut is much related to the quality of the color and clarity.
The grade D-F emerald diamonds are more in demand than the same color grade of other diamonds because the diamond doesn’t hide the color, it rather retains it. The clarity grade that is most recommended for an emerald diamond is the VS2 clarity grade. This is the grade that gives you the best value for your money. This is unlike many other diamond cuts that allow you to settle for as low as an S1 clarity grade. The emerald diamond makes inclusions very visible, so the clarity required is a lot higher than other diamonds.
The emerald cut was named after the gemstone called “emerald”. The beginning of this cut date back to as far as the 1500s, that’s some 500 years ago. The emerald gem is very soft, vulnerable and prone to damage. Therefore stonecutters had to look for a way to cut the stone without having to damage the stone. A stonecutter made the discovery that the stone is more stable with stepped facets. Gems always have stepped facets run in parallel lines along their length.
The emerald cut diamonds are diamonds that are cut following a pattern known as “step cut”. This type of cut follows a pattern of cutting the stone like a step in receding lines that are parallel to each other.
The emerald cut was made popular between 1920 and 1939 during the Art Deco period. It was in 1940 that this type of diamond cut was given its present state. This diamond cut does leave no single room for mistakes. This is because imperfections can be seen very easily in the stone with this type of cut. The most important part of this cut is the perfection it requires.

Analysis of the Emerald Cut
The emerald cut is known to have up to 50-58 facets. The number of facets may differ among different emeralds and it basically depends on the pavilion and the number of rows on its crown. The length to width ratio that is appropriate for the emerald cut is 1.5 to 1 or 1.7 to 1.
The shape of the emerald cut is rectangular. The corners of the shape are trimmed and the facets are parallel to the girdle. The emerald cut, when compared to other types of cuts like the round cut or the princess cut, appears like it is less brilliant. This is true but it actually has a different sparkle that is more subtle than the others. When you view the emerald diamond from the top, it has a pattern that displays an “on and off” effect. This kind of effect is different from the ones that are commonly seen in diamonds that have smaller facets. The emerald cut diamonds are actually less brilliant than other popularly known diamond cut and this is because the purpose of the emerald cut is not to emphasize the brilliance of the diamond’s fire but to show off the clarity of the diamond.
The step-cut (which is also the same as diamond cut) has a kind of effect known as “hall of mirrors effect”. This effect or illusion creates flashes of white light that are bright when compared to the dark planes that are within the steps of the diamond. The quality required for the color and clarity of the emerald cut is very high because it is known to be a very unforgiving cut. This is due to the fact that impurities and inclusions that are present in the cut can be very easily noticed. That is why it requires a high level of perfection. The attractiveness of the cut is much related to the quality of the color and clarity.
The emerald cut has an elongated shape that makes it appear like it is longer and a lot bigger than it actually is. It also makes the fingers of the women wearing them to appear longer and of course more elegant. The surface area of the emerald diamond is known to be about 5 greater than the surface area of round brilliant diamonds that have the same weight.
The ideal depth of the emerald diamond cut is between 60 to 65 and the table also ranges from 61 percent to 68 percent.
There is a little amount of the stone that is lost while cutting this stone because the shape of the cut is closer to the original shape of the diamond. This influences the price of this diamond and makes it popular among buyers.
According to the GIA (Gemological Institute of America), the cuts of the emerald diamond is not graded. The GIA does not assign any cut grade to the emerald cut diamonds. So if you happen to come across any cut grades classification, that’s obviously no from GIA. It most likely is the jeweler that assigned the cut grades by themselves. This, on its own, is not a bad thing but you must be sure that you can verify this cut grade by yourself before going ahead to purchase any diamonds.
In other to maximize the beauty of a diamond, the diamond cut is a very important factor. So, it’s always a good thing for you to know the specifications for the ideal cut. The table below would serve as a guide for you to evaluate the cut of an emerald diamond.
| EXCELLENT | VERY GOOD | GOOD | FAIR | POOR | |
| TABLE | 61 – 69 | 57 – 60 or 70 – 72 | 54 – 56 or 73 – 74 | 51 – 53 or 75 – 79 | < 51 or > 79 |
| DEPTH | 61 -67 | 59 – 60.9 or 67.1 – 70 | 57 – 58.9 or 70.1 to 74 | 54 – 56.9 or 74.1 – 79 | < 54 or > 79 |
| GIRDLE | Very thin to slightly thick | Very thin to slightly thick | Very thin to thick | Very thin to very thick | Ex. Thin to Ex. Thick |
| CULET | None | Very small | Small | Medium | >Medium |
Although, most emerald diamonds have a rectangular shape there are some others that have square shapes as well. This square shaped emerald diamond can be easily confused for the Asscher cut which is considered a square cut diamond by the GIA. Each of these diamonds has its precise measurements and their different length to width ratio.
The length to width ratio is measured by dividing the length of the diamond by its width. The length of the diamond to its width helps us to know the proportion of the diamond with its shape, which can either be square or rectangle, in the case of an emerald diamond. It gives us an idea of how a diamond will appear when we look at it from the top. An example is this, if the length of the diamond is 6mm and the width is 4mm. to get the length to width ratio, you have to divide the length by the width, that is, 6mm/4mm. this gives us a length to width ratio of 1.5.
The table below shows the guide for the length to width ratio of the two different shapes of the emerald cut diamond.
| EXCELLENT | VERY GOOD | GOOD | FAIR | POOR | |
| Square | 1.00 – 1.03 | 1.00 – 1.03 | 1.04 – 1.05 | 1.06 – 1.08 | > 1.08 |
| Rectangle | 1.40 – 1.50 | 1.30 – 1.39 or 1.51 – 1.60 | 1.20 – 1.29 or 1.61 – 1.80 | 1.15 – 1.19 or 1.81 – 1.90 | < 1.15 or > 1.90 |

The Color of Emerald Cut Diamonds
Diamonds mostly come in a variety of colors, color is one of the attributes in emerald cut diamond which makes it more noticeable. It retains more color than any other diamond shapes. Apparently color comes in different grade which makes some diamond look colorless and unable to detect the color once it is set in a ring and especially when it is placed in an environment that has a color that is different from the normal ones that are used in grading the color of diamonds. One of the factors that affect a diamond’s apparent color is the color of the mounting itself. Generally, step-cut diamonds do not show a lot of brilliance and they do not hide colors as well. The GIA has a system for grading the color of emerald diamonds. Grade D – F is primarily considered colorless. This color grade of the emerald diamond is more commonly in demand than other grades. Some customers are may be willing to pay for this grade of an emerald diamond while others may prefer the slightly warmer colors. Grade G – H is considered as warmer colors.
- Grade color D: All color of a diamond are usually considered white, even though they consist of varying degrees of color. Grade color D is usually scale (colorless)
- Grade color E: It is different between Grade color D and Grade color E but the difference can be detected with the mere eye it can only be detected by a gemologist in side by side comparison, and rarely by the untrained eye.
- Grade color F-H: Emerald GIA Grade color on a scale from D-H is the most colorless. When you look at Emerald Diamond from Grade D-H with the naked eye it is likely not to notice much of any difference.
- Grade color I – Z: Emerald Grade color that is on a scale of the grades I – Z mostly contain easily noticeable brown or yellow tint. Especially Emerald Diamond of grade J, with the higher naked eye you can easily notice a slight yellow tint. However, the J color diamond may appear whiter when set in yellow gold.
| EXCELLENT | VERY GOOD | GOOD | FAIR | POOR | |
| < .50 ct. | D – G | H – I | J – K | L – M | >M |
| .51 – 1.0 ct. | D – F | G | H – I | J – K | >K |
| 1.0 – 2.0 ct. | D – F | D – F | G | H – I | >I |
| >2.0 ct. | D – F | D – F | G | H – I | >I |
| Fluoro | None | Faint | Medium | Strong – Very Strong | Strong – Very Strong |

The Clarity of Emerald Cut Diamond
The Gemology Institute of America (GIA) has a classification grade for the clarity of emerald diamonds. The scale ranges from the diamonds that do not have inclusions at all to the ones that have inclusions that are very noticeable. The grading is as follows.
- IF – Internally Flawless
- VVS1 – Very Very Small Inclusions 1
- VVS2 – Very Very Small Inclusions 2
- VS1 – Very Small Inclusions 1
- VS2 – Very Small Inclusions 2
- SI1 – Small Inclusions 1
- SI 2 – Small Inclusions 2
- I1 – Inclusions 1
- I1 – Inclusions 2
The table of an emerald diamond is like a window that is unobstructed, this means you can look straight through to the center of the emerald diamond. If there are any inclusion or blemishes at the center, it will be seen very clearly. The pavilion of the stone and the crown as well are shallow when compared to other diamonds, which is why the emerald diamond is not as bright or has a lot of fire like other stones. Rather than being fiery, they rather increase the clarity of the diamond. So, very little flaws and impurities are easily noticed in emerald diamonds. That’s why they are viewed as unforgiving diamonds.
The most important thing to consider when buying an emerald diamond is to ensure that it is clean to the eye. If you can spot an impurity, no matter how small, it isn’t advised that you buy it. This is especially very important if you’re looking to buy one in the SI1 or SI2 grade. The VS2 clarity grade is, however, the most recommended. If you’re not sure of your eyesight, however, or you don’t want to take any risks regarding the clarity of the diamond that you’re about to buy, it is advisable for you to get an expert who can help you ascertain its clarity before you make the purchase. The chart below gives a general guideline on the clarity of emerald diamonds.
| EXCELLENT | VERY GOOD | GOOD | FAIR | POOR | |
| .50 ct. | FL – VS2 | SI1 | SI2 | I1 | > I1 |
| .51 – 1.0 ct. | FL – VS1 | VS2 | SI1 | SI2 | > SI2 |
| 1.0 – 2.0 ct. | FL – VVS1 | VS1 – VS2 | SI1 | SI2 | > SI2 |
| > 2.0 ct. | FL – VVS2 | VS1 | VS2 | SI1 | > SI1 |
The Carat Weight of Emerald Cut Diamonds
The prices of emerald shapes diamond vary considerably, so your focus should be on getting the right proportions, polish, symmetry, color, clarity, and price within the range of carat weight that you want. The carat weight of the diamond actually differs from the size of the diamond. Although, it’s not always the case with all types of diamond, an increase in the size of the diamond results in an increase in the carat weight.
| MM Size | Carat Weight |
| 6.0 x 4.0 | 0.50 ct. |
| 6.5 x 4.5 | 0.75 ct. |
| 7.0 x 5.0 | 1.00 ct. |
| 7.5 x 5.5 | 1.50 ct. |
| 8.0 x 6.0 | 1.75 ct. |
| 8.5 x 6.5 | 2.00 ct. |
| 9.0 x 7.0 | 2.50 ct. |
| 10.0 x 7.5 | 3.00 ct. |
A guide to choosing the right emerald diamond based on the cut, color, clarity, carat weight and price (especially when working with a restricted budget):
An excellent choice
Criteria:
- The carat weight should be at least 1.0 carat weight.
- The polish and the symmetry must be very good or excellent.
- The color should be D and G.
- The clarity should be from SI1 or higher than that.
- It should not have any fluorescence.
- The length to width ratio should be 0.9 – 1.05 if the emerald diamond is square or 1.5 to 1.6 if the emerald diamond is rectangular.
A very good choice
Criteria:
- The carat weight should be at least 0.90 carat weight.
- The symmetry and polish must be between good and excellent.
- The color should be at least H and above.
- The clarity should be from SI1 or above that.
- It is best if it does not have any fluorescence. But medium or faint fluorescence is still acceptable.
- The length to width ratio should be 0.95 – 1.05 if the emerald diamond is square shaped but if it is rectangular, the length to width ratio should be 1.45 – 1.65.
A good choice
Criteria:
- The carat weight should be at least 0.80 carat weights.
- The symmetry and polish should be good or very good.
- The color should not be a grade lower than I. it should be I and above.
- The clarity should not be below SI1 clarity grade. It should be this or higher than this.
- It is also best if it does not have any fluorescence. But if it does, the fluorescence should be faint or medium blue. Those are acceptable.
- The length to width ratio should be 0.95 – 1.05 if the emerald diamond is a square shaped one. But otherwise, if it is rectangular, the length to width ratio should be 1.4 – 1.68.
An important tip for buying an emerald cut diamond is this, you must always look to maintain the right measurement while not compromising on the ideal cut. For example, if you have 3 different emerald cut diamonds
One is ideally cut, has a 1.0 carat weight and, measurements of 6.4mm x 4.7mm.
The second one also has a carat weight of 1.0, the measurements are 6.5mm x 4.8mm, it looks a little bigger than the first one and is also ideally cut.
The third one has a carat weight of 0.97, the measurements are 6.5mm x 4.8mm, it is ideally cut.
The third diamond is most likely to be cheaper than the first two because it has the least carat weight. But this is the preferred option that we recommend for you. They are all ideally cut and the length to width ratio is very similar to a negligible difference. The only difference is the carat weight which influences the price heavily. The question you should ask yourself is why pay more for something no one can see or even notice? Bingo! You got it, you can save yourself that extra cash. Thank me later!