The cut and color of a diamond are two of the most important components of the 4Cs used for evaluating a diamond. The cut is the most important component followed by the color of the diamond, however, both are unarguably relevant.
Diamond Cut:
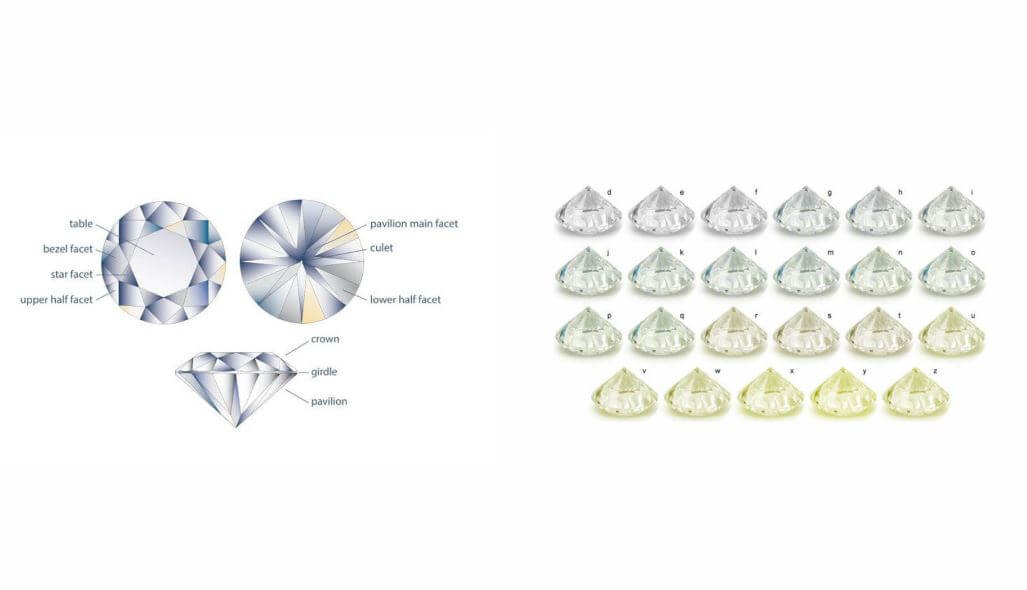
A diamond’s cut refers to the quality of the different components that make up the beauty and attractiveness of the diamond. The diamond’s polish, symmetry, culet, girdle, crown angle, and pavilion angle are some of the attributes that determine the cut of a diamond.
There are 3 main attributes to the cut of a diamond. They are brilliance, fire, and scintillation.
The brilliance of a diamond refers to the ability of the diamond to properly combine the white lights that it reflects to create a brightness around it that is visibly seen by the observer. This beautiful brightness of the diamond is known as the brilliance of the diamond.
The fire of a diamond refers to a series of spectacularly beautiful colors flashing all over the different parts of the diamond. These flashes of color are caused by the dispersion of white light that comes into the diamond by the diamond’s facet which acts as a prism.
The scintillation of a diamond occurs when a diamond is moved, there is usually some beautiful reflection of light and dark in some areas of the diamond. This contrast between white and black causes the scintillation that adds to the beauty of the diamond.
All of these three cut attributes are usually more pronounced and well combined in a diamond that is well-cut. The amount of beauty that a diamond shows reflects the cut grade of the diamond. A diamond with an excellent cut will have an outstanding beauty due to the high level of brilliance, fire, and scintillation that it possesses. While a diamond with a poor cut will look no more than an ordinary stone, dull and without life in it.
Grades of Diamond Cut
The depth of a diamond’s pavilion is one factor that significantly affects the cut of a diamond. If the pavilion depth is too deep or too shallow, the diamond will not be able to reflect all the light that comes into it. It will lose some of the light and this will affect the brilliance of the diamond. But if the pavilion depth is ideal, the diamond will lose less light and be more brilliant. The same applies to the culet of the diamond. The grade of the culet determines how much light the diamond will lose. It might not lose any light and be very brilliant or lose most of its light and be very dull.
There are 5 different grades of diamond cut according to the GIA. GIA put factors like diamond’s relative weight, the thickness of the diamond’s girdle, diamond symmetry, etc. to grade the cut of the diamond on a scale from excellent to poor.
Excellent cut: They show the maximum amount of brilliance, fire, and scintillation. Almost all the light that enters the diamond is reflected back. This grade of diamond is the best available grade for the cut of a diamond.
Very good cut: Similar to the excellent grade, the diamond reflects most of the light that enters into it, although not as much as the excellent grade. These diamonds usually have a steeper crown angle and higher crown height which gives it its splintery pattern, and they exhibit a high level of sparkle, fire, and brilliance.
Good cut: The diamond reflects many of the light that comes into it and has an average beauty. The pavilion and crown angle of these diamonds are steep. They usually have a low crown height and a shallow crown angle. These diamonds are not usually very brilliant and do not exhibit much fire.
Fair cut: These diamonds do not have a lot of fire and brilliance. They do not get to reflect most of the light that comes into them because they lose them easily. Their crown and pavilion angle is shallow and this gives the diamond a dark appearance. They are not recommended.
Poor cut: This is the least grade of diamond cut. Diamonds with this cut grade are usually very dull in appearance. This is because they lose most of the light that comes into them. So they lack the brilliance and fire that diamonds have. They look nothing more than an ordinary rock and are definitely not recommended.
Diamond Color:
This is the second most important parameter of the diamond 4Cs used to estimate the value of a diamond. The presence or absence of color in diamonds is used as a measure for estimating how good or bad a diamond really is. The value of a diamond is affected strongly by the colors in it except in cases where the diamonds are considered fancy colors based on the type of color in it.
Diamonds are naturally expected to be colorless, and while there are some diamonds that are truly colorless, there are more diamonds that have colors. The color in diamond varies to different degrees, while it is very little in some diamonds, it is very obvious in some others. This generally affects the overall appearance of the diamond.
Based on the amount of color in a diamond, the GIA has a color scale used to grade and evaluate a diamond’s color.
Diamond Color Scale
The diamond color scale runs from grade D – Z. the different grades are further divided into 5 groups (colorless diamonds, near colorless diamonds, faint color diamonds, very light color diamonds, and light color diamonds).
Group D-F (Colorless diamonds): These diamonds are truly colorless and this is why they are able to fit in with any setting you choose. They are however the most expensive as well.
Group G-J (Near colorless diamonds): These diamonds have a little color in them but it is not very unless under proper inspection. This group can be further divided into two G-H and I-J. The G-H appears more like the colorless diamonds, while the I-J tends towards the fair color diamonds. The difference between these two is quite glaring if you hold them both side by side.
Group K-M (faint color diamond): These diamonds have a yellow tint that is obvious even to the naked eye. The yellow coloration is faint but it is still visible. This makes the diamond less desirable and cheaper than others above it.
Group N-R (very light color diamonds): Diamonds in this group have easily noticeable color. This color might be a brown tint or a yellow tint. The prices for these diamonds are extremely low because the demand for them is equally very low. They are often referred to as top light brown.
Group S-Z (light color diamonds): These diamonds have a yellow coloration and surprisingly are more in demand in the market than the group above them. The obvious yellow tint of these diamonds has made people consider it a “yellow stone” (they are however not fancy stones). The grading of the intensity of the yellow diamond actually starts with fancy light. So the U – X grades and the Y – Z grades are considered as replacements for the faint yellow and the light yellow diamonds.
Diamond Buying Tips
- The brilliance and sparkle of a diamond are determined by its cut.
- Prioritize the diamond cut. If the color and clarity grade of the diamond is very high and the cut is poor, the diamond will still appear dull.
- If you are buying a grade I or J grade diamond, you should consider setting it in a yellow gold setting.
- Color becomes more visible in diamonds as the diamond size increases.
- Prioritize the color of a diamond over the diamond clarity and especially over the carat weight.
- Make sure the diamond you are buying is certified.
Executive Summary
The cut and color of diamonds are two distinctively important components of the diamond 4Cs. The cut is unarguably the most important and should be given the utmost priority when buying diamonds. The cut of a diamond is determined by the proportions of certain diamond components, like the girdle thickness, culet, crown angle, pavilion angle, symmetry, etc. the proportion of all of these diamond parameters determines the cut of a diamond.
A diamond’s cut itself determines the brilliance, fire, and scintillation in a diamond. All of these 3 play important roles in the overall brilliance of the diamond. A well-cut diamond is able to combine all of these 3 together to give a bright and beautiful diamond.
The grade of a diamond cut measures how beautiful the diamond is based on how much light the diamond is able to reflect. The 5 diamond cut grades are excellent, very good, good, fair and poor cut grades, which are determined by factors like the relative weight of the diamond, symmetry, girdle thickness, etc.
Diamonds are naturally colorless gemstones, so the presence of color in them is seen as an aberration. This is why diamond color is can also be used to measure or evaluate the value of a diamond. The color in a diamond is graded by the GIA and this results in the color grade of diamonds.
The color grade of diamonds is grouped with letters ranging from D-Z. This color grade is further grouped into 5 groups; colorless diamonds, near colorless diamonds, faint diamonds, very light color diamonds, and light color diamonds.
Colors in diamonds normally reduce the value of the diamond except in the case of fancy diamonds, where the color can range from blue, green, pink, yellow, etc. learn more about fancy diamonds here.