Executive summary
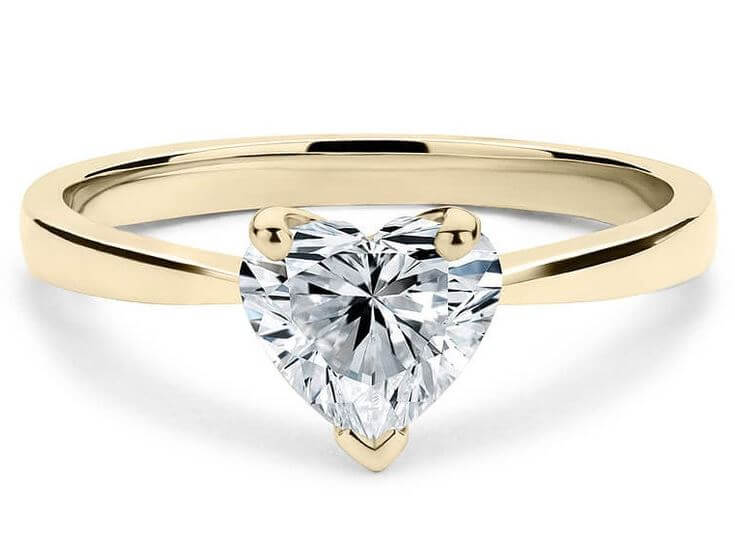
The diamond has the shape of “love”. That’s why it is named a heart cut diamond. One of the most important attributes of this diamond is symmetry. This is very important because it is expected that the two sides or two halves of the heart are equal. The cleft (the line that separates the two lobes) must be very sharp and distinctive. The wings of the diamond too (which are the sides of the diamond that curves down towards the pointed edge) should be slightly round in shape.
The size of the heart diamond plays an important role in the perception of colors in the diamond. The setting is also important as it also determines how color is perceived in the diamond. So it is strongly advised that you determine the setting you’re going to be placing the diamond in first before buying the diamond.
The ideal color grade for the heart cut diamond is the G grade. This is the grade that gives you the best quality for your price.
Clarity is a very important thing when dealing with the heart cut diamond because it is very easy to notice any inclusions in the diamond. This is a very unforgiving cut that does not hide impurities in it at all. It requires a rare skill set and certain techniques to cut this diamond perfectly, this is why it is one of the rarest and most expensive diamond cut in the market.
Before buying the heart diamond, there are certain things that are very important to a good heart diamond and you must pay attention to them;
- The diamond size
- The diamond symmetry
- The bow tie effect
- The heart silhouette
All of these have to be considered as important criteria when buying a heart diamond.
The heart cut diamond might be common in today’s world but that doesn’t make it any less recent than other diamond cuts. As a matter of fact, it is a very old diamond cut. This diamond shape dates back as far as the end of the 15th century (the late 1400s). At that time it was considered to be a sign of royalty. This diamond was used to symbolize friendship among royalties. In the year 1562, Queen Elizabeth of England received a heart shaped diamond from the Mary Queen of Scotland. At about the same time, a wealthy diamond merchant gifted nobleman Cardinal de Richelieu a heart shaped diamond. From that time the diamond shape has been known to be a symbol of goodwill.
Down the century and over the years, the heart shaped diamond became more accessible to a lot of people. It is no longer exclusive to just royalties and noblemen of the society anymore. The problem that has persisted with it down the years though has been the fact that it is very rare and also very expensive. The reason for this is the fact that this special diamond shape requires a rare skill set from the cutter. Not just the skillset but also special tools are required to make this cut. So it’s not usually readily available.

Analyzing the Cut of the Heart Cut Diamond
The heart cut diamond is obviously shaped like a “love”, that is why it is named the heart cut. We all believe that true love lives in the heart. It would be a good idea to buy this diamond shape as a show of love for your loved one. But you have to pay attention to the symmetry of the diamond.
One important characteristic of the heart shaped diamond is the symmetry. This is very important because it is expected that the two sides or two halves of the heart are equal. The cleft (the line that separates the two lobes) must be very sharp and distinctive. The wings of the diamond too (which are the sides of the diamond that curves down towards the pointed edge) should be slightly round in shape.
The average length to width ratio of a heart shape diamond is 1.00 but this could vary based on the preference of the buyer. Some buyers may prefer their heart shape diamond to be thinner and longer while some would prefer it to be wider. This preference would determine what length to width ratio to go for. Whether lower than 1.00 (which will be wider) or higher than that (which will be thinner). Heart shaped diamond usually come in different silhouettes which may be fat or narrow depending on the buyer’s preferred length to width ratio. The setting which the buyer prefers to place the diamond would also determine the length to width ratio. If the diamond would be set in a pendant, the ideal length to width ratio would be between 1.05 – 1.15 (the shape would be narrow). If the diamond would be set in a solitaire ring, the ideal length to width ratio would be 0.85 – 1.00 (the shape would be slightly wider).
The heart cut has about 56 – 58 facets which make it reflect light very well. This implies that this diamond cut is a brilliant cut.
The table below can serve as a guideline for you to consider when evaluating the cut of the heart cut diamond.
| EXCELLENT | VERY GOOD | GOOD | FAIR | POOR | |
| Table | 53 – 63 | 52 or 64 – 65 | 51 or 66 – 68 | 50 or 69 – 70 | < 50 or > 70 |
| Depth | 58 – 62 | 56 – 57.9 or 62.1 – 66 | 53 – 55.9 or 66.1 – 71 | 50 – 52.9 or 71.1 – 74 | < 50 or > 74 |
| Girdle |
Very thin – slightly thick |
Very thin to slightly thick | Very thin to thick | Very thin to very thick | Ex. Thin to ex. Thick |
| Culet | None | Very small | Small | Medium | > medium |
| Length to width ratio | 0.95 – 1.02 | 0.89 – 0.94 or 1.03 – 1.05 | 0.83 – 0.87 or 1.06 – 1.10 | 0.80 – 0.83 or 1.11 – 1.15 | > 0.80 or < 1.15 |

Evaluating the Color of the Heart Cut Diamond
There are different color grades for evaluating the color of a diamond. The grades start from grade D all the way down to grade Z. the most expensive and sought after color grades are usually those diamond grades from D – F according to the GIA, diamonds in these grades are colorless. The color grade of a diamond determines how much color is in the diamond. Grade D diamonds are colorless diamonds and the color of the diamonds increases down the grading system. This means that grade I diamonds have more color in them than grade G diamonds. And although grade F diamonds are considered colorless, they are not as colorless as grade D diamonds. It means that grade F diamonds still have little colors in them (even though they are largely considered as colorless). But this difference between the grade D and grade F diamonds cannot be noticed, especially not by the naked and untrained eye. In reality, the difference between the color grades (especially consecutive grades) is hardly noticeable. What is obviously noticeable as the difference between these color grades is the prices. The color grade of a diamond determines the price of the diamond. Diamonds with higher color grades usually have higher prices but as you move down the grade from D – Z, the price of the diamonds reduces.
The color that is perceived in a diamond by the eye depends on certain factors. The diamond size (how big or small the diamond is) plays a vital role in the perception of a particular color in the diamond. Another factor that determines the perception of color in a diamond by the naked eye is the setting in which the diamond is placed. So it is strongly advised that you determine the setting you’re going to be placing the diamond in first before buying the diamond. You’ll find this to be an important move because you can easily determine the length to width ratio that would go with the setting. And you can also decide if you like the perceived color that the setting gives your diamond.
The ideal color grade for the heart cut diamond is the G grade. This is the grade that gives you the best quality for your price. You get exactly what you want as regards the color of a diamond without necessarily breaking the bank trying to buy the grade D diamond. If you opt to buy diamond grades between D – F, the color of the diamond would usually appear icy-white. Do not forget that the setting of your diamond influences the perceived color of the diamond. So your preferred setting can help you make a choice on whether to go high up the color grade or to go a little bit down the color grade. For instance, if you prefer that the diamond is set in a yellow gold setting, you can settle for a lower color grade. You don’t have to go for D – F, grades H – K will do the work just perfectly.
Your personal preference as a buyer also comes into play when determining the color grade that you are buying. If you prefer cooler colors, you should just go for the D – F grades. But if you prefer diamonds with warmer colors, then you can settle for G – H color grades.
The table below would help you evaluate the color of the heart cut diamond.
| EXCELLENT | VERY GOOD | GOOD | FAIR | POOR | |
| < .50 ct. | D – G | H – I | J – K | L – M | > M |
| .51 – 1.0 ct. | D – F | G | H – I | J – K | > K |
| 1.0 – 2.0 ct. | D – F | D – F | G – H | I – J | > J |
| >2.0 ct. | D – F | D – F | G | H – I | > I |
| Fluorescence | None | Faint – medium | Strong | Very Strong | Very Strong |

Evaluating the Clarity of the Heart Cut Diamond
The clarity of a diamond describes how much of inclusions and blemishes are seen in the diamond. There are diamonds that appear clean there, without any inclusions (which should be what a good clear and buyable diamond should be like). But in reality they are not perfect or flawless, they actually have inclusions in them. The GIA has a grade of clarity for diamonds ranging from the Internally Flawless (IF) grade to the Inclusions 2 (I2) grade. These grades define varying degrees of clarity and blemish that can be found in the diamond.
It is important to note that when buying a diamond, the ideal criteria to note for clarity is whether or not the diamond has inclusions that are noticeable or visible to the naked eye. The second thing is the location of the inclusion (if it is present in the diamond and also noticeable). It is more ideal if there are no visible inclusions in the diamond. But if you’re going to compromise on this, make sure that the inclusions are at the edge of the diamond. This is to ensure that the inclusions can be masked by the setting the diamond is placed in. The diamond setting should not expose the edges of the diamond.
Clarity is a very important thing when dealing with the heart cut diamond. We already mentioned earlier that this diamond cut is very rare and expensive because it requires certain techniques, skillset, and tools to create this cut. Any slight mistake when cutting this diamond shape will be very easily noticed. I am not just talking about the diamond being asymmetrical or the wings bulging outwards, inclusions are also a part of this. If the cutter fails to cut this diamond right and it has a little inclusion, just a little inclusion, it’ll be more easily noticed than in other diamond cuts. If you’re looking for a diamond that does well in hiding inclusions, you have to move past the heart cut diamond. If there’s anything it does at all, this diamond cut is good at exposing impurities. This is one of the reasons why the heart shaped diamond is so expensive. The buyer is at a disadvantage when buying this diamond shape. Because you’re forced to go a little bit higher up the clarity grade than you would with other diamond shapes that hide impurities. For instance, if you are to buy a pear shaped diamond, you can decide to stick to an S1 or S2 clarity grade because of the diamond’s ability to mask impurities. This is not the case for the heart cut diamond. If you want to buy an equivalent heart cut diamond, you need to go up to the VS2 clarity grade at least. Trust me, the difference in prices between consecutive clarity grades can be quite a deal. So you’re forced to spend more to get a good heart cut diamond.
However, the general rule of thumb for the clarity of diamonds when purchasing is to make sure that the diamond is eye clean (that is, it does not have any inclusions visible to the naked eye). If you’re following this, your major aim would not be the clarity grade of the diamond. It could help you save some cash. It might be rare but you could find an S1 clarity heart cut diamond as well. But if you’re considering the best clarity for an affordable price, the VS2 is the ideal clarity. On the other hand, some people just decide to buy the flawless diamond or others high up the clarity grade because they do not want to take any chances with the clarity of their diamond and also because they can afford it. So after it’s all been said and done, it really boils down again, to the buyer’s preference and very importantly as well, the size of their budget.
The table below would serve as a guide for evaluating the clarity of a heart cut diamond before making the purchase.
| EXCELLENT | VERY GOOD | GOOD | FAIR | POOR | |
| .50 ct. | FL – VS2 | SI1 – SI2 | I1 | I2 | > I2 |
| .51 – 1.0 ct. | FL – VS1 | VS2 – SI1 | SI2 | I1 – I2 | > I2 |
| 1.0 – 2.0 ct. | FL – VVS2 | VS1 – VS2 | SI1 – SI2 | I1 | > I1 |
| > 2.0 ct. | FL – VVS2 | VS1 – VS2 | SI1 | SI2 | > SI2 |
Evaluating the Carat Weight of the Heart Cut Diamond
The size of the heart cut diamond is very important. The size determines the weight and the unit used for measuring the weight is the carat weight. Different carat weights correspond to different diamond sizes. The larger the size of the diamond, the bigger the carat weight is. The carat weight measurement is also used to determine the price of the diamond. Typically, the higher the carat weight, the higher the price of the diamond.
The table below gives an idea of the carat weight that corresponds to different sizes of the heart shape diamond.
| Size of heart shape diamond | Corresponding carat weight |
| 4.13 x 4.13 mm | 0.25 ct. |
| 5.21 x 5.21 mm | 0.5 ct. |
| 5.96 x 5.96 mm | 0.75 ct. |
| 6.56 x 6.56 mm | 1.0 ct. |
| 7.07 x 7.07 mm | 1.25 ct. |
| 7.51 x 7.51 mm | 1.5 ct. |
| 7.91 x 7.91 mm | 175 ct. |
| 8.27 x 8.27 mm | 2.0 ct. |
| 8.60 x 8.60 mm | 2.25 ct. |
| 8.91 x 8.91 mm | 2.5 ct. |
| 9.19 x 9.19 mm | 2.75 ct. |
| 9.46 x 9.46 mm | 3.0 ct. |
| 9.72 x 9.72 mm | 3.25 ct. |
| 9.96 x 9.96 mm | 3.5 ct. |
| 10.19 x 10.19 mm | 3.75 ct. |
| 10.42 x 10.42 mm | 4.0 ct. |
Before making that ultimate choice to purchase a particular diamond, there are things that you must ensure are appropriately set in their right order. The peculiarity of the heart shaped diamond means you must be strict with what you want in your diamond so that you don’t end up with something laughable instead of a good diamond.
The diamond size: The size of the heart shaped diamond that you’re purchasing should be more than 0.5 ct. otherwise, the beautiful features of the heart cut diamond would not be noticed. The bigger the diamond is the better the features are shown.
The diamond symmetry: This is very important, and has been mentioned earlier. The heart has two equal halves and this is expected to be seen in the heart shape diamond. It should be symmetrical, the cleft should be sharp. The wings should be a little rounded and should meet perfectly in the middle.
Bow tie effect: Like many other fancy diamond cuts, the heart cut diamond is also prone to having the bow-tie effect. The bowtie effect is when there’s a dark band across the middle of the diamond in the shape of the bow tie.
The heart silhouette: The silhouette of your choice affects the length to width ratio of the diamond. The silhouette can either be narrow or wide. If you prefer a wider silhouette, then you know that a diamond that fits in will require a smaller length to width ratio than the classic 1.00.
In all, you must make sure that whatever diamond you’re buying is certified. Common certification includes the GIA ad AGS certification. This gives you some guarantee for what you’re buying. The certification is however not an excuse for you to not view the diamond you’re purchasing. Take a look at it yourself. Have a feel of it. Make sure it is really eyeing clean and does not have the bowtie effect. That’s how to buy yourself a quality diamond.